-
tel:
+86-13606193016 -
email:
info@suhangmachine.com
Innovative Applications and Technical Excellence in PU Shutter Door Systems
Jan 14, 2026
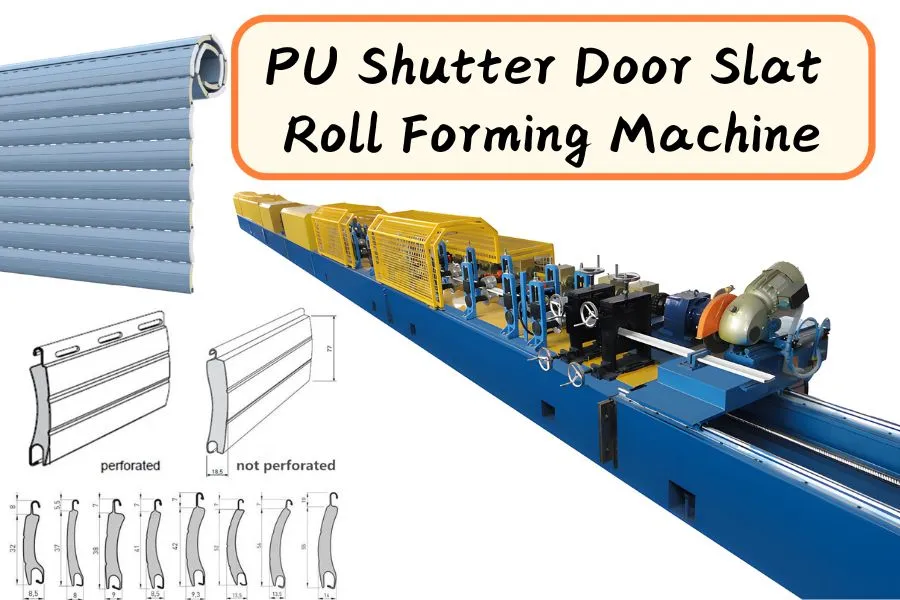
Innovative Applications and Technical Excellence in PU Shutter Door Systems
Introduction: Beyond Basic Door Functionality
Modern PU shutter door systems have evolved from simple access points to sophisticated building components that significantly impact energy efficiency, operational performance, and building intelligence. These advanced door systems, manufactured using precision roll forming technology, offer solutions that address the complex challenges of contemporary industrial, commercial, and institutional buildings. This comprehensive guide explores the innovative applications, technical considerations, and implementation strategies for high-performance PU shutter door systems.
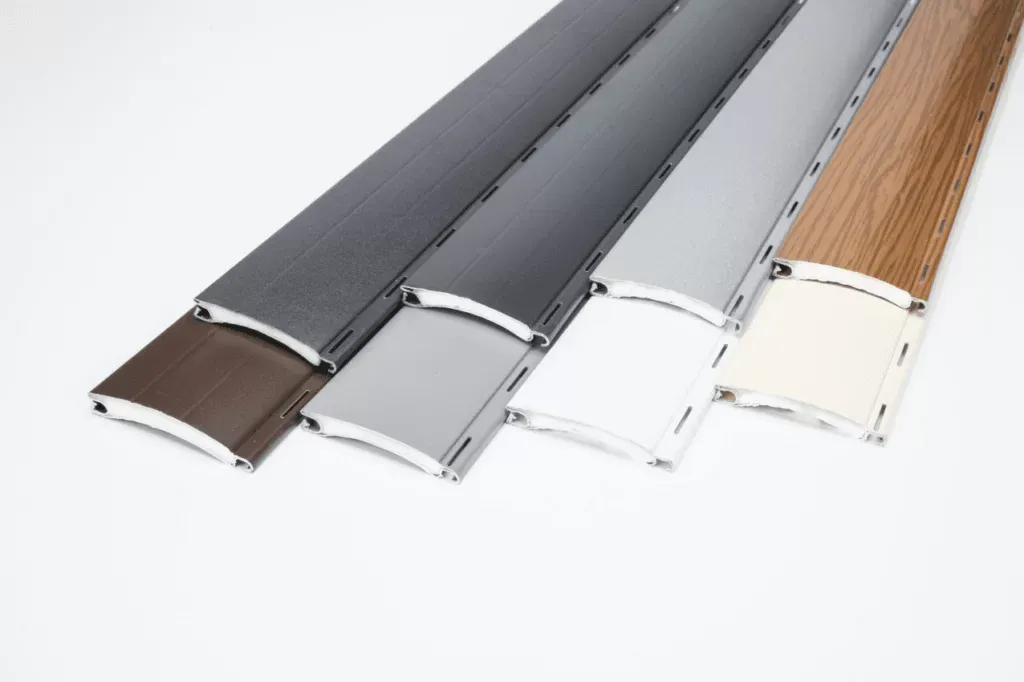
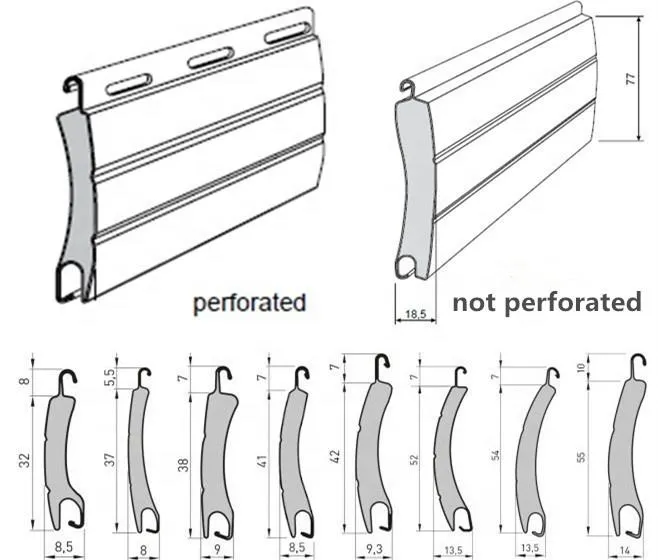

Advanced Architectural and Industrial Applications
Smart Industrial Solutions
Intelligent Door Systems
-
Automated Operation: Integrated control systems with sensor technology
-
Energy Management: Thermal performance monitoring and optimization
-
Security Integration: Access control and surveillance system compatibility
-
Maintenance Monitoring: Predictive maintenance capabilities through IoT sensors
Specialized Industrial Environments
-
Clean Room Applications: Pharmaceutical and electronics manufacturing
-
Hazardous Material Areas: Chemical and biological containment
-
High-Traffic Facilities: Distribution centers and logistics hubs
-
Extreme Environment Protection: Foundries and cold storage facilities
Commercial and Retail Innovations
Large-Scale Commercial Projects
-
Shopping Mall Integration: Brand-specific design customization
-
Office Complex Solutions: Corporate identity and energy efficiency
-
Hospitality Industry: Hotel and resort security and aesthetics
-
Entertainment Venues: Arena and theater loading systems
Retail-Specific Applications
-
Storefront Security: After-hours protection with thermal efficiency
-
Seasonal Adaptation: Temperature control for varying merchandise
-
Brand Enhancement: Custom colors and finishes for brand identity
-
Operational Efficiency: Rapid opening/closing for customer flow management
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
Innovative Design Concepts
Dynamic Door Systems
-
Multi-Section Designs: Segmented doors for partial opening
-
Variable Insulation: Different R-values for various building zones
-
Integrated Lighting: LED systems within door structures
-
Smart Glass Integration: Transparent insulation options
Sustainable Building Integration
-
Passive House Compatibility: Ultra-high insulation values
-
Solar Integration: Support for photovoltaic systems
-
Rainwater Management: Integrated collection systems
-
Natural Ventilation: Controlled airflow management
Technical Engineering Excellence
Structural Design Considerations
Load Analysis and Performance Requirements
-
Wind Load Engineering: Calculation based on location, height, and exposure
-
Thermal Performance: U-value and R-value optimization
-
Operational Loads: Cycle life and mechanical stress analysis
-
Safety Factors: Emergency operation and failure mode analysis
Material Science Applications
-
Advanced Steel Alloys: High-strength, corrosion-resistant formulations
-
Aluminum Options: Lightweight alternatives with thermal breaks
-
Foam Technology: Variable density and formulation optimization
-
Surface Technologies: Advanced coatings for durability and aesthetics
Performance Standards and Certification
International Standards Compliance
-
EN 13241-1: Industrial, commercial, and garage doors
-
ASTM E283: Air leakage performance
-
ISO 10211: Thermal bridges in building construction
-
DIN 18055: Thermal insulation for doors
Comprehensive Testing Protocols
-
Thermal Testing: Hot box method for U-value determination
-
Air Infiltration Testing: Pressure differential performance
-
Structural Testing: Load capacity and operational durability
-
Fire Resistance Testing: For specialized applications requiring fire ratings
Installation Excellence and Commissioning
Pre-Installation Planning
Site Assessment Protocol
-
Structural Evaluation: Opening condition and load capacity verification
-
Environmental Analysis: Climate considerations and exposure assessment
-
Utility Coordination: Integration with building systems
-
Access Planning: Installation methodology and safety considerations
Design Integration Process
-
Architectural Coordination: Seamless integration with building design
-
Functional Requirements: Operational needs and performance criteria
-
Future Planning: Maintenance access and potential upgrades
-
Value Engineering: Cost-performance optimization
Installation Methodology
Phase 1: Preparation and Framework
-
Opening Preparation: Structural modifications and reinforcement
-
Track System Installation: Precision alignment of guide systems
-
Motor and Control Mounting: Mechanical and electrical preparation
-
Safety System Installation: Sensors and emergency controls
Phase 2: Door Assembly and Integration
-
Slat Assembly: Sequential installation of insulated panels
-
Mechanical Connection: Interlocking and securement of components
-
Sealing System Installation: Weather seals and thermal breaks
-
Operational Testing: Manual and automated function verification
Phase 3: Commissioning and Handover
-
Performance Testing: Thermal and operational verification
-
Safety System Validation: Emergency function testing
-
Client Training: Comprehensive operation and maintenance instruction
-
Documentation Delivery: Manuals, certifications, and warranties
.webp)
Critical Installation Considerations
Environmental Adaptations
-
Extreme Climate Areas: Enhanced insulation and sealing
-
High Humidity Environments: Corrosion protection and moisture management
-
Seismic Zones: Earthquake-resistant mounting systems
-
Coastal Locations: Salt spray resistance and protection
Safety and Compliance Requirements
-
Emergency Egress: Code-compliant emergency operation
-
Electrical Safety: Proper grounding and circuit protection
-
Accessibility Standards: ADA compliance where required
-
Local Code Compliance: Specific regional requirements
Maintenance and Performance Optimization
Proactive Maintenance Schedule
Regular Maintenance Protocol
-
Monthly: Visual inspection and operational check
-
Quarterly: Mechanical system lubrication and adjustment
-
Semi-Annually: Seal inspection and thermal performance verification
-
Annually: Comprehensive system review and calibration
Specialized Care Procedures
-
Thermal Performance Monitoring: Infrared inspection for heat loss
-
Seal System Maintenance: Replacement and adjustment of weather seals
-
Control System Updates: Software and hardware maintenance
-
Surface Care: Cleaning and protection of finishes
Performance Optimization Strategies
Energy Efficiency Enhancement
-
Seal Optimization: Minimizing air infiltration
-
Insulation Upgrades: Enhanced foam formulations or additional layers
-
Operational Efficiency: Optimized opening/closing cycles
-
Integration with Building Automation: Coordinated climate control
Lifespan Extension Techniques
-
Preventive Maintenance: Proactive component replacement
-
Environmental Protection: Additional protective measures
-
Upgrade Pathways: System enhancement opportunities
-
Monitoring Systems: Continuous performance tracking
Industry Innovations and Future Directions
Emerging Technologies
Smart System Integration
-
IoT Connectivity: Real-time performance monitoring
-
Predictive Analytics: AI-driven maintenance scheduling
-
Energy Management: Integration with building energy systems
-
Adaptive Control: Systems that learn from usage patterns
Material Science Advances
-
Aerogel Integration: Ultra-high performance insulation
-
Phase-Change Materials: Dynamic thermal regulation
-
Self-Healing Coatings: Automatic repair of surface damage
-
Bio-Based Foams: Sustainable insulation alternatives
Design Evolution
Architectural Trends
-
Minimalist Aesthetics: Clean lines and hidden mechanisms
-
Custom Finishes: Architectural-grade surface treatments
-
Transparent Options: Insulated glass integration
-
Modular Systems: Scalable and reconfigurable designs
Sustainability Focus
-
Circular Economy: Design for disassembly and recycling
-
Carbon Neutral Manufacturing: Offset production emissions
-
Lifecycle Analysis: Comprehensive environmental impact assessment
-
Renewable Integration: Compatibility with renewable energy systems
Market Analysis and Business Opportunities
Global Market Trends
-
North America: Growing emphasis on energy efficiency and security
-
Europe: High standards for thermal performance and sustainability
-
Asia-Pacific: Rapid industrialization driving demand
-
Middle East: Extreme climate adaptation requirements
Business Development Strategies
-
Specialized Manufacturing: Narket-specific product development
-
System Integration: Complete door solution provision
-
Maintenance Services: Ongoing support and optimization
-
Training and Certification: Industry education programs
Economic and Environmental Impact Analysis
Cost-Benefit Considerations
-
Initial Investment: Manufacturing equipment and setup costs
-
Operational Savings: Energy efficiency and maintenance cost reduction
-
Lifecycle Costs: Total cost of ownership analysis
-
Return on Investment: Payback period calculation
Environmental Benefits
-
Energy Conservation: Reduced heating and cooling requirements
-
Carbon Footprint Reduction: Lower energy consumption emissions
-
Material Efficiency: Optimized use of resources
-
Waste Reduction: Manufacturing process optimization
Conclusion: The Future of Intelligent Door Systems
PU shutter door systems manufactured through advanced roll forming technology represent more than just access points—they are intelligent building components that contribute significantly to operational efficiency, energy conservation, and building performance. As technology continues to advance and sustainability becomes increasingly important, these systems will play a crucial role in the evolution of smart, efficient buildings.
The convergence of precision manufacturing, advanced materials science, and digital technology creates unprecedented opportunities for innovation in door system design and performance. For building owners, architects, and facility managers, understanding the full potential of modern PU shutter door systems enables informed decisions that balance performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
The future of door systems lies in smarter integration, sustainable materials, and designs that respond to evolving building requirements and environmental challenges. As we move toward more connected, efficient, and sustainable built environments, advanced PU shutter door systems will continue to be at the forefront of building technology innovation.
Ready to explore advanced PU shutter door solutions? Our technical team offers comprehensive support for manufacturing, design, and implementation tailored to your specific requirements and applications.



Related News

October 26, 2016
The Most Successful Engineering Contractor





